Scientists Discover How Correlated Disorder Boosts Superconductivity

Superconductivity is a unique state of matter in which electric current flows without any energy loss. In materials with defects, it typically emerges at very low temperatures and develops in several stages. An international team of scientists, including physicists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that when defects within a material are arranged in a specific pattern rather than randomly, superconductivity can occur at a higher temperature and extend throughout the entire material. This discovery could help develop superconductors that operate without the need for extreme cooling. The study has been published in Physical Review B.
Superconductivity is a state in which electric current flows through a material without any energy loss. In conventional conductors, part of the energy is converted into heat, but in superconductors, this does not occur—current flows freely and does not weaken. Today, superconductors are used in applications such as MRI machines, where superconducting coils generate strong magnetic fields. In the future, superconductors may also be integrated into systems that require lossless power transmission and high-speed signal processing. The challenge is that nearly all superconductors function only at temperatures below -140 °C, which limits their practical use. To make them more viable, physicists are working to raise their operating temperature and improve stability.
Researchers from the HSE MIEM Centre for Quantum Metamaterials, in collaboration with colleagues from MEPhI, MIPT, and the Federal University of Pernambuco, Brazil, have shown that superconductivity can be made more stable by controlling the placement of defects. Defects are deviations from a material’s ideal crystal lattice, such as excess or missing atoms, impurities, and distortions. They usually disrupt the movement of electrons and weaken superconductivity, but it is impossible to eliminate them entirely, especially in multicomponent materials. Rather than eliminating these imperfections, the scientists have proposed arranging them in a specific pattern. This type of defect distribution is known as correlated disorder.

Alexei Vagov
'Imagine a crowd of people moving chaotically in different directions—that’s a classic example of disorder. Now imagine the same crowd moving in a complex but coordinated pattern, like a mass dance—that illustrates correlated disorder,' says Alexei Vagov, Professor at the HSE Tikhonov Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics. 'In superconductors, it turns out that this kind of order within disorder causes defects to actually enhance superconductivity.'
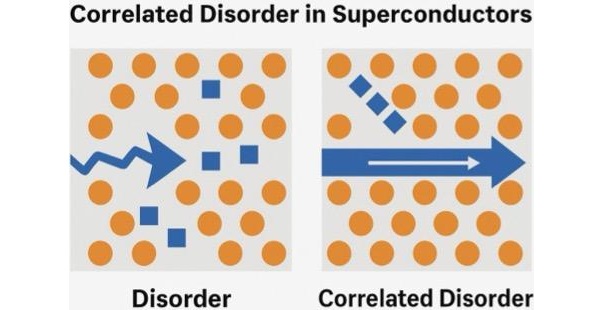
In materials with defects, superconductivity typically develops in two stages. First, isolated regions appear where superconductivity begins to emerge. Then, as the temperature drops, these regions connect, allowing current to flow throughout the entire sample. Scientists have modelled a two-dimensional superconductor with varying defect distributions—from random to correlated, where impurities are interconnected. The results show that when disorder in the material is coordinated rather than chaotic, the transition happens immediately: superconductivity emerges simultaneously throughout the entire system.
The scientists believe these findings could aid in the development of thin superconducting films, whose structures closely resemble the model used in the study. When synthesising such films, it is possible to control the placement of defects in advance, which is useful both for testing the theory and for creating materials with specified properties.
'Controlling the placement of defects at the microscopic level could enable the creation of superconductors that operate at much higher temperatures—potentially even at room temperature. This would transform superconductivity from a laboratory rarity into a technology used in everyday devices,' comments Alexei Vagov.
The study was conducted with support from the Ministry of Education and Science, Grant 075-15-2025-010, and HSE University's Basic Research Programme within the framework of the Centres of Excellence project.
See also:
IDLab: Fascinating Research, Tough Deadlines, and Academic Drive
The International Laboratory of Intangible-driven Economy (IDLab) was established at the HSE campus in Perm 11 years ago. Its expertise in data processing and analysis allows researchers to combine fundamental studies with applied projects, including the development of risk and cybersecurity models for Sber. The head of the laboratory, Professor Petr Parshakov, and Senior Research Fellow Professor Mariya Molodchik spoke to the HSE News Service about IDLab’s work.
HSE Tops Ranking of Universities Participating in Priority 2030 Programme
The Russian Ministry of Science and Higher Education has published an updated list of participants in the Priority 2030 programme. A total of 106 universities will receive support this year. HSE University was included in the first group and topped the ranking.
HSE Psycholinguists Launch Digital Tool to Spot Dyslexia in Children
Specialists from HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain have introduced LexiMetr, a new digital tool for diagnosing dyslexia in primary school students. This is the first standardised application in Russia that enables fast and reliable assessment of children’s reading skills to identify dyslexia or the risk of developing it. The application is available on the RuStore platform and runs on Android tablets.
HSE Scientists Optimise Training of Generative Flow Networks
Researchers at the HSE Faculty of Computer Science have optimised the training method for generative flow neural networks to handle unstructured tasks, which could make the search for new drugs more efficient. The results of their work were presented at ICLR 2025, one of the world’s leading conferences on machine learning. The paper is available at Arxiv.org.
Physicists Propose New Mechanism to Enhance Superconductivity with 'Quantum Glue'
A team of researchers, including scientists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that defects in a material can enhance, rather than hinder, superconductivity. This occurs through interaction between defective and cleaner regions, which creates a 'quantum glue'—a uniform component that binds distinct superconducting regions into a single network. Calculations confirm that this mechanism could aid in developing superconductors that operate at higher temperatures. The study has been published in Communications Physics.
Neural Network Trained to Predict Crises in Russian Stock Market
Economists from HSE University have developed a neural network model that can predict the onset of a short-term stock market crisis with over 83% accuracy, one day in advance. The model performs well even on complex, imbalanced data and incorporates not only economic indicators but also investor sentiment. The paper by Tamara Teplova, Maksim Fayzulin, and Aleksei Kurkin from the Centre for Financial Research and Data Analytics at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences has been published in Socio-Economic Planning Sciences.
Mistakes That Explain Everything: Scientists Discuss the Future of Psycholinguistics
Today, global linguistics is undergoing a ‘multilingual revolution.’ The era of English-language dominance in the cognitive sciences is drawing to a close as researchers increasingly turn their attention to the diversity of world languages. Moreover, multilingualism is shifting from an exotic phenomenon to the norm—a change that is transforming our understanding of human cognitive abilities. The future of experimental linguistics was the focus of a recent discussion at HSE University.
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.
New Models for Studying Diseases: From Petri Dishes to Organs-on-a-Chip
Biologists from HSE University, in collaboration with researchers from the Kulakov National Medical Research Centre for Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Perinatology, have used advanced microfluidic technologies to study preeclampsia—one of the most dangerous pregnancy complications, posing serious risks to the life and health of both mother and child. In a paper published in BioChip Journal, the researchers review modern cellular models—including advanced placenta-on-a-chip technologies—that offer deeper insights into the mechanisms of the disorder and support the development of effective treatments.
Using Two Cryptocurrencies Enhances Volatility Forecasting
Researchers from the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences have found that Bitcoin price volatility can be effectively predicted using Ethereum, the second-most popular cryptocurrency. Incorporating Ethereum into a predictive model reduces the forecast error to 23%, outperforming neural networks and other complex algorithms. The article has been published in Applied Econometrics.


